This page presents the methodology, experimental design, and preliminary findings from my ongoing Master’s thesis research on evaluating LLM-generated test quality through mutation analysis.
Research Questions
This thesis addresses a critical gap in AI-driven software testing: Can LLMs generate tests that actually catch bugs, not just achieve high code coverage?
- RQ1: What percentage of mutants can LLMs successfully detect through their generated test cases?
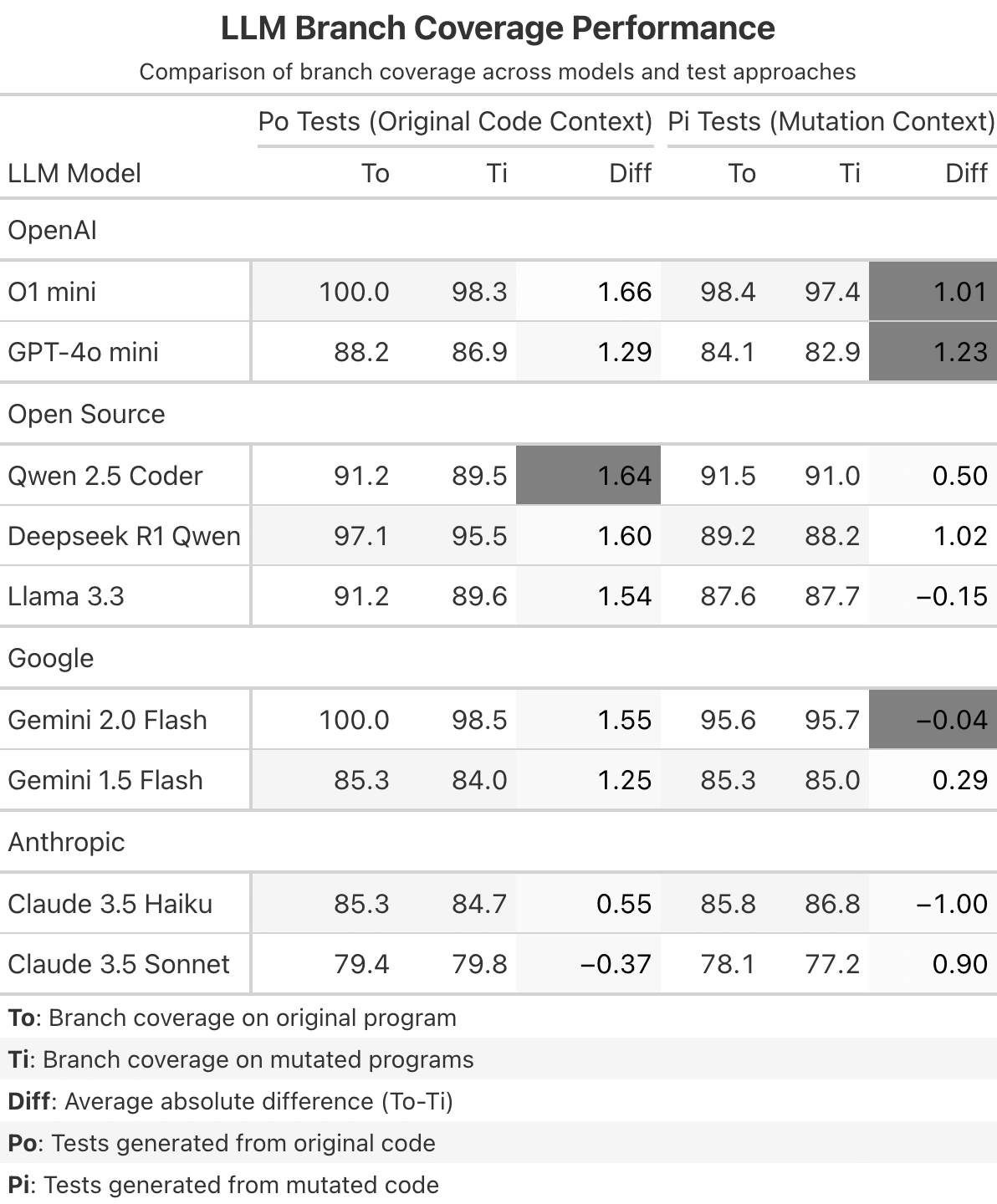
- RQ2: Does providing the mutated code as context improve detection rates compared to the original code?
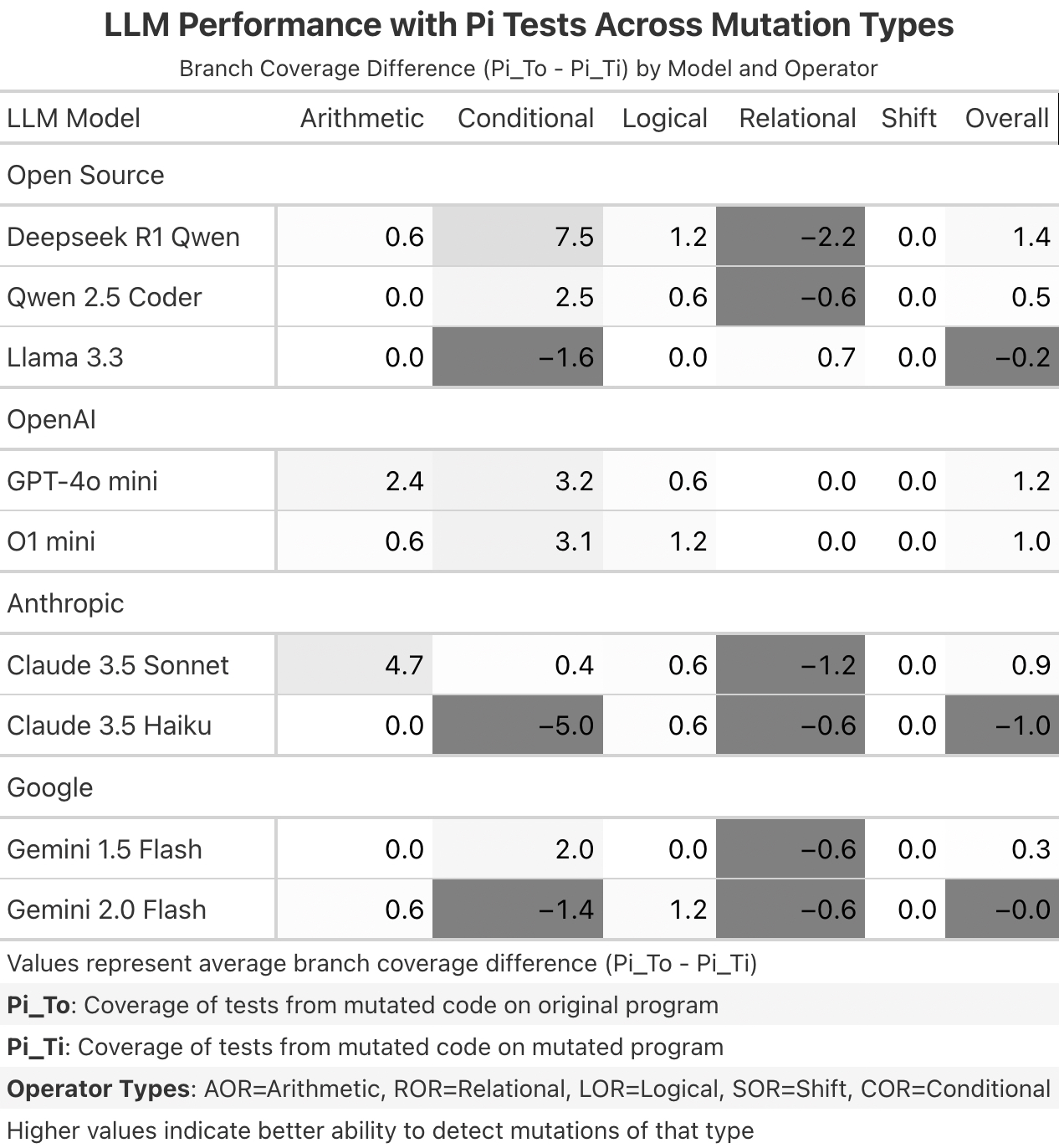
- RQ3: How does detection rate vary across different LLM models and mutation types?
- RQ4: How does test effectiveness vary across different method types?
System Architecture
Multi-Container Orchestration
The system isolates the AI agent from the execution environment using Docker:
Agent Container (Python 3.11+)
- Handles LLM communication and orchestration
- Tech Stack:
pydantic-ai,pandas,groq,openai - Runs experiment notebooks
Java-Projects Container (Java 11 / Maven)
- Compiles code, runs tests, generates coverage reports
- Tech Stack: OpenJDK 11, Maven 3.8.6, JUnit 4.11, JaCoCo, Major Mutation Framework
Inter-Container Communication
Containers communicate via a file-based trigger system over shared volumes:
def trigger_maven_build(timeout=60):
trigger_path = shared_volume / "triggers" / "run_maven.trigger"
status_path = shared_volume / "triggers" / "maven_status.done"
trigger_path.touch() # Signal Java container
# Wait for completion
start_time = time.time()
while not status_path.exists():
if time.time() - start_time > timeout:
raise TimeoutError("Java build hung.")
sleep(1)
status_path.unlink() # CleanupMethodology

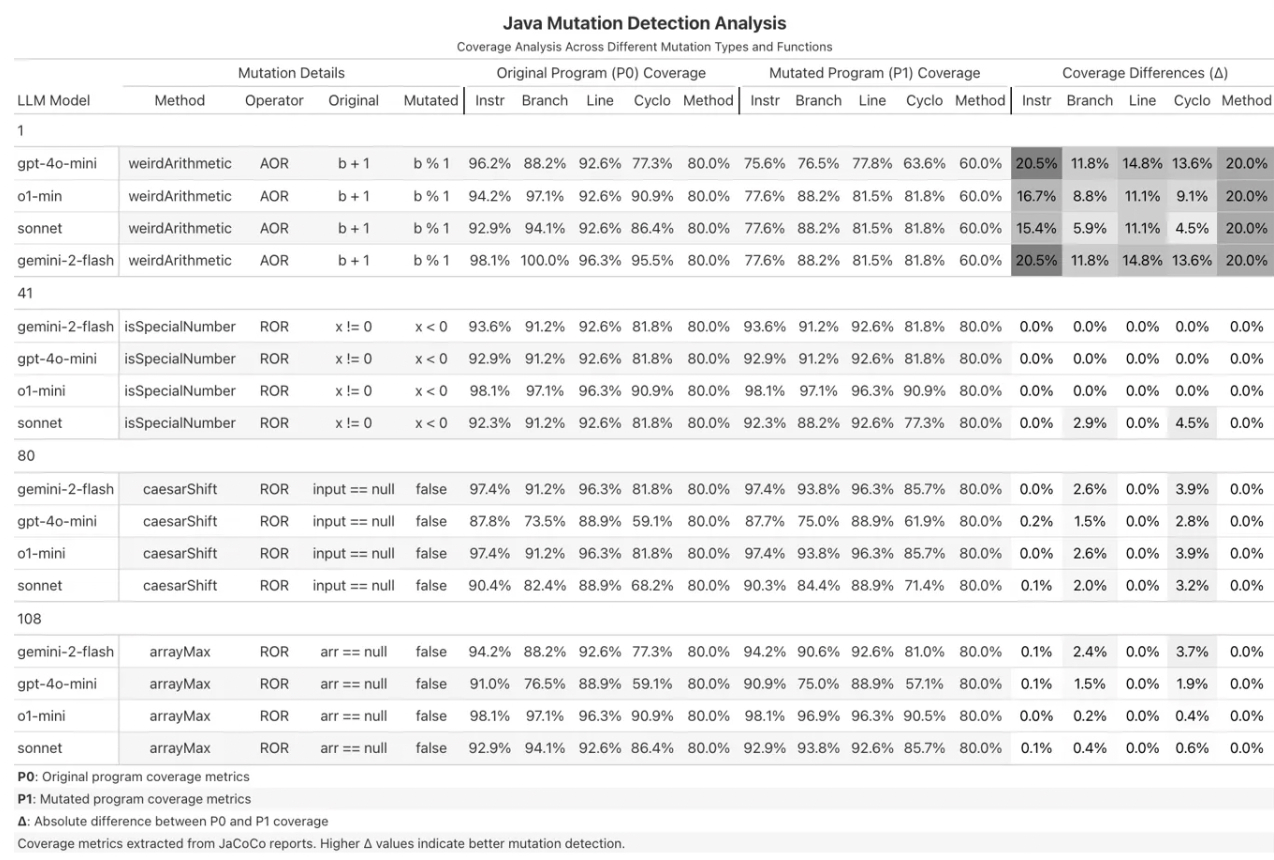
Figure 1. Workflow for generating mutants using the Universal Mutator with custom RegEx-based rules and Comby integration with localized injections based on predefined mutation types (AOR, COR, ROR, LVR, EVR).
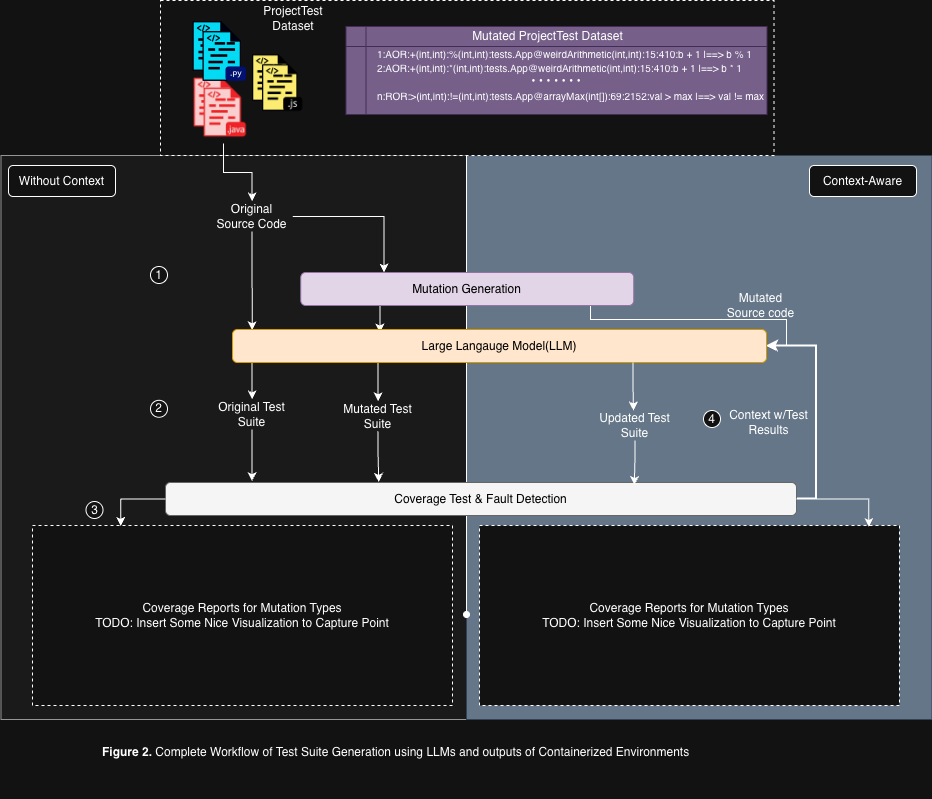
Figure 2. Complete Workflow of Test Suite Generation using LLMs and outputs of Containerized Environments
Example: The Subject Application
Custom Java utility class (App.java) designed to test different LLM reasoning capabilities:
weirdArithmetic(int a, int b)- Complex arithmetic, bitwise operations, ternary logic (targets AOR mutations)isSpecialNumber(int x)- Boolean logic and conditional branching (targets LOR/ROR mutations)caesarShift(String input, int shift)- String manipulation, loops, character arithmeticarrayMax(int[] arr)- Array traversal, null handling, boundary conditions
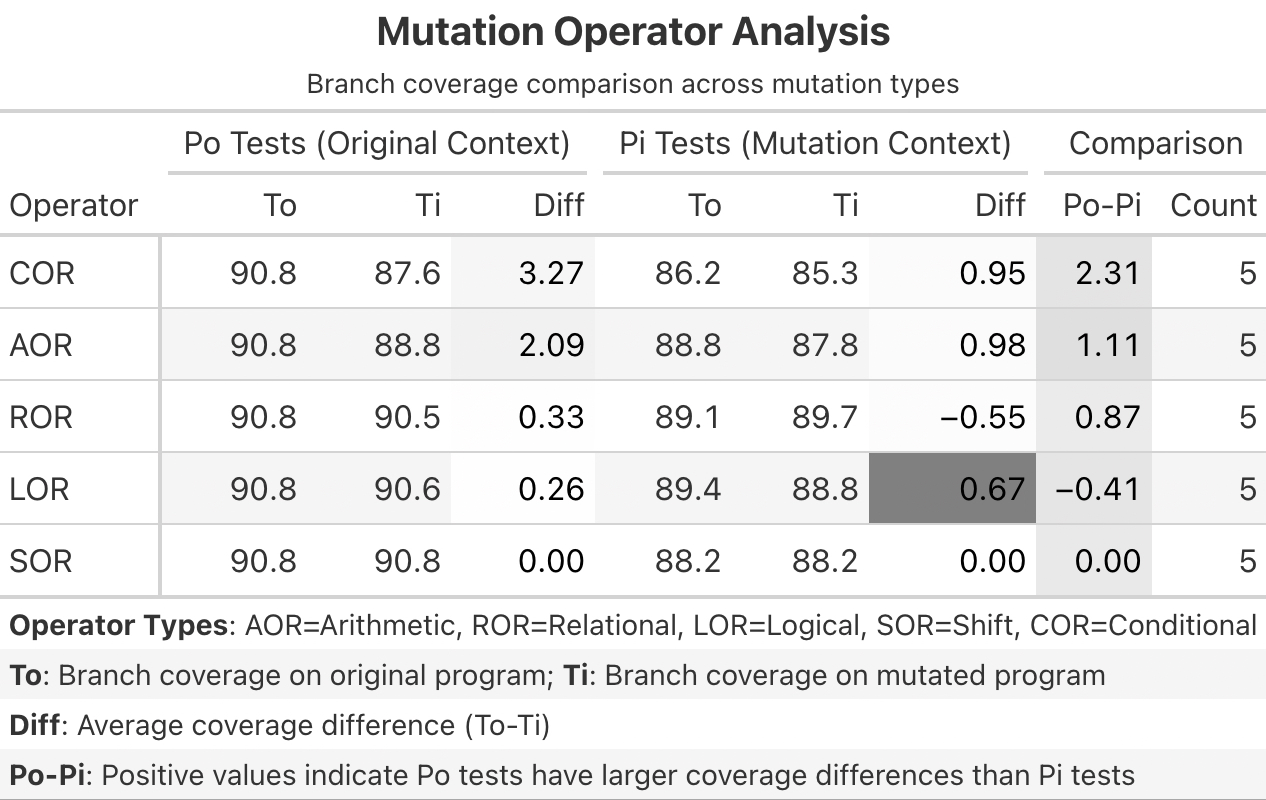
Experimental Design: P0 vs P1
Phase 1: P0 Generation (Baseline)
- LLM sees the Original Code
- Prompt: “Generate a test suite for this code”
- Goal: Can the LLM write tests robust enough to accidentally catch unseen bugs?
Phase 2: P1 Generation (Targeted)
- LLM sees the Mutated Code (without being told it’s buggy)
- Prompt: Same as P0
- Goal: If the LLM sees the bug, does it write a test targeting that logic path?
Kill Criteria
A mutant is “killed” if there’s a significant Coverage Delta (Δ) or test failure difference when running the same test suite against Original vs Mutant code.
Models Evaluated
Proprietary: GPT-4o-mini, o1-mini, Claude 3.5 Sonnet/Haiku, Gemini 1.5/2.0 Flash
Open Source (via Groq): Llama-3.3-70b, Qwen-2.5-Coder-32b, DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32b
Dataset
- Total Mutants: ~117 generated by Major Framework
- Selected Subset: 25 mutants chosen for diversity
- Mutation Types: AOR (Arithmetic Operator Replacement), ROR (Relational Operator Replacement), LOR (Logical Operator Replacement)
Technical Implementation
Directory Structure
shared/
├── original_tests/ # P0 Results
│ └── {model_name}/
│ ├── AppTest.java
│ ├── p0_coverage.csv
│ └── coverages/
│ └── mut_{id}.csv
└── mutants/
└── {id}/
└── mut_gen_tests/
└── p1_evaluation/ # P1 Results
└── {model_name}/
├── AppTest.java
├── p0_coverage.csv
└── p1_coverage.csvOrchestration Logic
P0 Optimization - Generate baseline tests once per model:
def process_initial_p0_generation(model_name: str, agent: Agent):
original_code = read_file(shared / "original" / "App.java")
test_code = generate_test_suite(original_code, agent, is_p0_context=True)
save_path = shared / "original_tests" / model_name / "AppTest.java"
save_file(test_code, save_path)
coverage = run_maven_test(test_code, original_code)
save_coverage(coverage, shared / "original_tests" / model_name / "p0_coverage.csv")P1 Targeted Testing - Generate mutant-specific tests:
def process_mutant_testing(mutant_id: str, model_name: str, agent: Agent):
mutant_code = read_file(shared / "mutants" / mutant_id / "tests" / "App.java")
original_code = read_file(shared / "original" / "App.java")
# Test P0 tests against mutant
test_p0_against_mutant(model_name, mutant_id, mutant_code)
# Generate P1 tests with mutant context
test_code = generate_test_suite(mutant_code, agent, is_p0_context=False)
save_and_test_p1_generation(test_code, model_name, mutant_id, original_code, mutant_code)Contributions
- Stable Orchestration Architecture: Python-based AI agents with Java/JS/Python build environments
- Context Sensitivity Analysis: Quantified whether “seeing the bug” leads to higher detection rates
- Model Benchmarking: Evaluated reasoning models, general models,and open/closed source models on mutation detection
If you would like to request code samples from this project, please email me.
